
Manufacturing isn’t what it used to be. Gone are the days when factories simply ran on human labor, mechanical tools, and paperwork. Today, data drives every decision, automation hums in the background, and agility decides who stays ahead. At the heart of this revolution sits (Manufacturing Execution Systems) the digital backbone that connects people, machines, and processes in real time.
But what does this mean for the future of manufacturing? Buckle up because the future isn’t just coming, it’s already here.
What is MES?
At its core, it’s manages, monitors, and synchronizes manufacturing processes in real time. Think of it as the nervous system of a factory constantly collecting data, analyzing it, and ensuring production runs like a well-oiled machine.
Why Manufacturing is Evolving
Global competition, rising customer expectations, and Industry 4.0 technologies are rewriting the rules. Manufacturers no longer have the luxury of guesswork; they need real-time insights, flexibility, and innovation to survive. MES is the answer.
The Core Definition of MES
If ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) handles planning, it’s handles the “doing.” It’s where production happens, data is tracked, and efficiency is measured.
How MES Bridges ERP and the Shop Floor
ERP is the brain, the shop floor is the hands, and it’s is the nervous system that keeps them in sync. Without it’s , gaps lead to errors, delays, and waste.
Key Features of MES
- Real-time production tracking
- Quality assurance and compliance monitoring
- Resource and workforce management
- Predictive maintenance
- Traceability across supply chains
Industry 4.0 and Digital Transformation
it’s is the backbone of Industry 4.0 integrating cyber-physical systems, IoT devices, and AI to create smart factories.
Benefits of MES for Modern Manufacturers
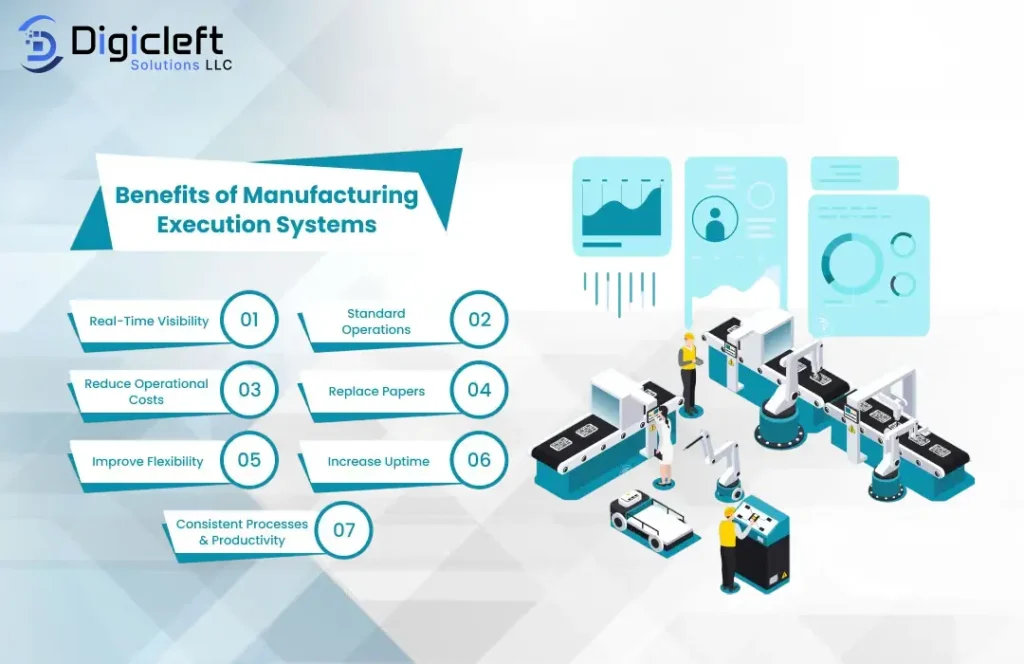
- Faster decision-making with real-time data
- Lower operational costs
- Higher productivity with fewer errors
- Competitive advantage in global markets
Challenges in Implementing
- Integration with legacy systems
- High upfront costs
- Workforce training requirements
But the long-term ROI outweighs the hurdles.
MES in Action – Real-World Applications
- Production Monitoring: Identifies bottlenecks before they cause delays.
- Quality Management: Ensures compliance with strict industry standards.
- Predictive Maintenance: Alerts operators about machine issues before downtime.
The Rise of Smart Factories
Smart factories are no longer science fiction. it’s makes them possible with IoT sensors, AI-driven analytics, and robotics working together.
Case Studies – Success Stories of MES
- Automotive: Faster production cycles and defect tracking.
- Pharma: Ensuring FDA compliance with traceability.
- Electronics: Managing complex, high-volume production with precision.
Conclusion – The Future is Now
it’s is shaping a new era of manufacturing that’s faster, greener, and customer-focused. The message is clear: adapt now or risk being left behind.
FAQs
Q1: What makes MES different from ERP?
ERP plans resources, while it’s executes and monitors production in real time.
Q2: Is MES only for large manufacturers?
No. Cloud-based it’s makes it accessible for SMEs as well.
Q3: How long does it take to implement it’s ?
Anywhere from a few months to over a year depending on plant size and complexity.
Q4: Can it’s integrate with AI tools?
Yes. AI-powered ]it’s predicts issues, optimizes workflows, and recommends improvements.
Q5: Which industries benefit most from MES?
Automotive, pharma, electronics, food processing, and any industry with complex production needs.


