
Preface
Have you ever tried to study a list of arbitrary data and realized it dissolved from your memory in a week? That’s the problem Cognitive Learning theory aims to fix. Unlike rote memorization, cognitive it’s focuses on how the brain understands, processes, and retains information essentially, how we learn to learn.
It isn’t just for students or teachers; it’s a life skill that improves problem-solving, adaptability, and creativity in any field.
The Core Principles of Cognitive Learning
Active Participation in Learning
You must actively engage with material asking questions, making connections, and applying concepts.
Building on Previous Knowledge
New information sticks better when connected to existing knowledge, like files in an organized system.
Understanding Over Memorization
Memorization has value, but true Learning comes from understanding the “why” and “how.”
The History and Evolution
From Behaviorism to Cognition
Early Learning models emphasized stimulus-response behavior. Later, psychologists recognized the internal processes.
Key Contributors
- Jean Piaget – Stages of cognitive development in children.
- Jerome Bruner – Discovery Learning and scaffolding.
- Lev Vygotsky – Social interaction in learning.
Cognitive Processes in Learning
- Perception – How sensory information is interpreted.
- Attention – Focus determines what gets processed.
- Memory – Transitioning from short-term “notepad” to long-term “library.”
- Problem-Solving – Learning to navigate complex situations, not just memorize answers.
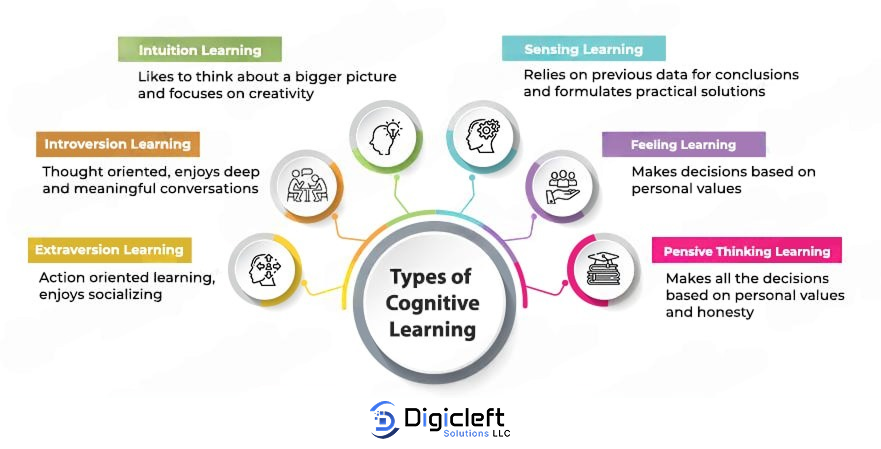
Types of Cognitive Learning
- Experiential Learning – Cognitive Learning by doing.
- Discovery Learning – Encourages exploration and uncovering knowledge.
- Observational Learning – Cognitive Learning by watching and imitating others.
Practical Applications in Education
Strategies for Teachers
- Use real-world examples.
- Ask open-ended questions.
- Encourage group discussions.
Designing Cognitive-Friendly Lessons
Incorporate visuals, storytelling, and hands-on activities.
Encouraging Self-Regulated Learning
Teach students how to plan, monitor, and evaluate their own progress.
Cognitive Learning in the Workplace
- Corporate Training – Shift toward interactive workshops.
- Encouraging Innovation – Understanding “why” fosters adaptability.
Tools and Techniques
- Concept Mapping – Visualizing connections between ideas.
- Mnemonics & Visualization – Turning abstract ideas into memorable images.
- Technology Integration – Personalized it’s via digital platforms (e.g., Digicleft Solution).
Cognitive Learning and Digital Transformation
- Online Learning – Flexible, self-paced study.
- AI Personalization – Adaptive it’s tailored to individuals.
Challenges
- Learner resistance to active methods.
- Time constraints compared to lectures.
- Misalignment with standardized tests.
Measuring Success
- Performance-Based Assessments – Projects, presentations, real-world tasks.
- Self-Assessment – Learners reflect on progress.
Future of Cognitive Learning
- Neuroeducation – Applying neuroscience to education.
- Virtual Reality – Immersive simulated environments.
Tips for Learners
- Set clear goals before learning.
- Practice reflective thinking.
- Connect new knowledge to prior experiences.
Common Misconceptions
- It’s not just for academics – Applies to cooking, sports, business, and more.
- It’s not anti-memorization – Memorization supports, but does not replace, understanding.
Conclusion
Cognitive it’s is a powerful approach that transforms how we acquire and apply knowledge. Whether you’re a student, teacher, professional, or lifelong learner, adopting these methods helps you think deeper, adapt faster, and retain information longer.
FAQs
1. What is the main goal of cognitive learning?
To promote deep understanding and the ability to apply knowledge in different contexts.
2. How is it different from rote learning?
Rote it’s focuses on memorization; cognitive it’s emphasizes comprehension and application.
3. Can cognitive it’s be used outside of school?
Yes workplaces, hobbies, and personal growth all benefit from it.
4. What role does technology play?
It enables personalized paths, interactive tools, and data-driven feedback.
5. How can I apply it today?
Engage actively with new material, connect it to what you know, and reflect regularly.


